When working on a Suzuki motorcycle, understanding the Suzuki 12 Pin Cdi Wiring Diagram is essential for troubleshooting electrical issues. This diagram shows the electrical connections between various components of the motorcycle’s ignition system, helping mechanics diagnose and repair problems effectively.
Why are Suzuki 12 Pin Cdi Wiring Diagrams essential?
Suzuki 12 Pin Cdi Wiring Diagrams are essential for the following reasons:
- They provide a visual representation of the electrical connections in the ignition system.
- They help mechanics identify the location of components and their respective wiring.
- They make it easier to trace electrical faults and diagnose issues accurately.
How to read and interpret Suzuki 12 Pin Cdi Wiring Diagrams effectively
Reading and interpreting Suzuki 12 Pin Cdi Wiring Diagrams can be daunting for some, but following these tips can make it easier:
- Start by identifying the key components in the diagram, such as the CDI unit, ignition coil, and spark plug.
- Follow the lines to trace the connections between components and understand how electricity flows through the system.
- Refer to the color-coding on the diagram to match wires with their corresponding functions.
Using Suzuki 12 Pin Cdi Wiring Diagrams for troubleshooting electrical problems
When faced with electrical issues on a Suzuki motorcycle, the Suzuki 12 Pin Cdi Wiring Diagram can be a valuable tool for troubleshooting. Here’s how to use it effectively:
- Identify the specific problem area on the motorcycle, such as a no-spark condition or intermittent starting issues.
- Refer to the wiring diagram to locate the components involved in the problematic circuit.
- Check for continuity, voltage, and resistance at various points in the circuit to pinpoint the source of the problem.
Importance of safety when working with electrical systems
Working with electrical systems, including using Suzuki 12 Pin Cdi Wiring Diagrams, requires caution and adherence to safety practices. Here are some key safety tips to keep in mind:
- Always disconnect the battery before working on any electrical components to prevent accidental shocks or short circuits.
- Use insulated tools and wear protective equipment, such as gloves and safety glasses, when handling electrical connections.
- Avoid working on electrical systems in wet or damp conditions to reduce the risk of electrical hazards.
Suzuki 12 Pin Cdi Wiring Diagram
12 Pin Cdi Wiring Diagram

12 Pin Cdi Wiring Diagram
Suzuki Cdi Wiring Diagram

Connection pin CDI | Motor Cycle
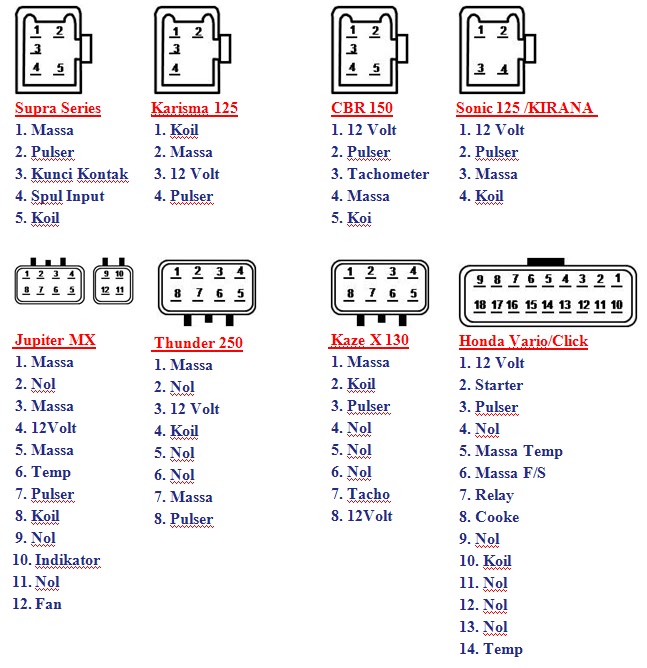
Suzuki Cdi Wiring Diagram

Pin CDI Wiring Diagram (Illustrated AND Explained!), 55% OFF

CDI wiring… | Suzuki GSX-R Motorcycle Forums Gixxer.com

96-96 750 GSXR CDI Wiring/ Offroad Gokart Project | Suzuki GSX-R
