Are you looking to understand the Nest Wiring Diagram Heat Pump for your HVAC system? This diagram is essential for properly wiring your heat pump to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. By following the wiring diagram accurately, you can avoid electrical issues and ensure that your heat pump operates smoothly.
Why Nest Wiring Diagram Heat Pump are Essential
- Ensures proper wiring of the heat pump system
- Prevents electrical issues and malfunctions
- Optimizes the efficiency of the heat pump
- Allows for easy troubleshooting of any wiring problems
How to Read and Interpret Nest Wiring Diagram Heat Pump
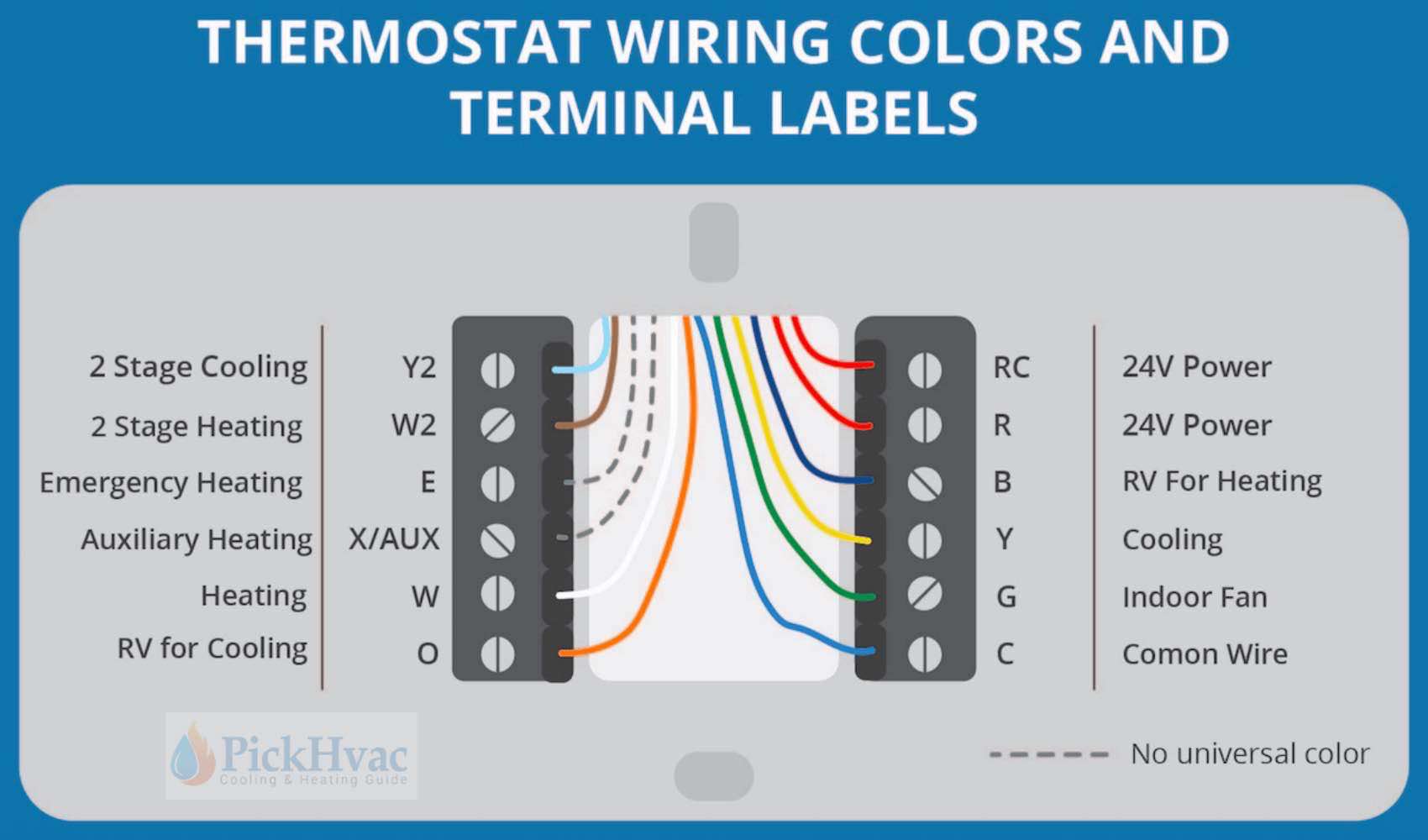
Reading and interpreting the Nest Wiring Diagram Heat Pump may seem daunting at first, but with a little guidance, it can be easily understood. Here are some tips to help you navigate the diagram:
- Identify the different components of the diagram, such as wires, terminals, and connections
- Follow the color-coding of the wires to ensure correct connections
- Pay attention to the labels and symbols used in the diagram
- Refer to the legend or key for any unfamiliar symbols or abbreviations
Using Nest Wiring Diagram Heat Pump for Troubleshooting Electrical Problems
When faced with electrical issues in your heat pump system, the Nest Wiring Diagram Heat Pump can be a valuable tool for troubleshooting. By following the diagram and checking the connections, you can pinpoint the source of the problem and make the necessary repairs. Here are some steps to effectively use the wiring diagram for troubleshooting:
- Inspect the wiring connections for any loose or damaged wires
- Refer to the wiring diagram to ensure all connections are correct
- Use a multimeter to test the continuity of the wires and components
- Consult the manufacturer’s guidelines for specific troubleshooting tips
Importance of Safety
When working with electrical systems and using wiring diagrams, safety should always be a top priority. Here are some safety tips and best practices to keep in mind:
- Turn off power to the heat pump before starting any work
- Use insulated tools to prevent electrical shocks
- Avoid working in wet or damp conditions to reduce the risk of electrocution
- Wear protective gear, such as gloves and safety goggles, to prevent injuries
Nest Wiring Diagram Heat Pump
Nest 3 Thermostat Wiring Diagram Heat Pump With Emergency Heat

Nest 3 Thermostat Wiring Diagram Heat Pump With Emergency Heat

Nest Thermostat Wiring Connections
Heat Pump Wiring Diagram Nest Nest Thermostat E Dual Fuel Wiring

Nest Wiring Diagram For Heat Pump – Easy Wiring

Nest Thermostat and Heat Pumps w/ Aux | Chris Tierney

Nest Thermostat Wiring Instructions

Wiring Diagram Nest Nest Heat Pump – Database | Wiring Collection
