Are you struggling to understand the Chevy 350 Starter Wiring Diagram? This article will guide you through the essential information you need to know about this crucial component of your vehicle’s electrical system.
Why Chevy 350 Starter Wiring Diagram are essential
Understanding the wiring diagram for your Chevy 350 starter is crucial for several reasons:
- It helps you identify the different components of the starter system.
- It enables you to troubleshoot any issues that may arise with the starter.
- It allows you to make necessary repairs or replacements with confidence.
How to read and interpret Chevy 350 Starter Wiring Diagram effectively
When looking at a Chevy 350 starter wiring diagram, it’s important to understand the symbols and colors used to represent the various components. Here are some key points to keep in mind:
- Identify the starter motor, solenoid, battery, ignition switch, and other relevant components.
- Follow the wiring paths and connections to ensure everything is properly connected.
- Pay attention to the color-coding of the wires to make accurate connections.
Using Chevy 350 Starter Wiring Diagram for troubleshooting electrical problems
When faced with electrical issues in your Chevy 350 starter system, the wiring diagram can be a valuable tool for troubleshooting. Here’s how you can use it effectively:
- Trace the wiring to identify any loose connections or damaged wires.
- Check for continuity using a multimeter to ensure all circuits are functioning properly.
- Refer to the wiring diagram to understand the sequence of operations and diagnose the problem accurately.
Importance of safety when working with electrical systems
Working with electrical systems, including Chevy 350 starter wiring, can be hazardous if proper precautions are not taken. Here are some safety tips to keep in mind:
- Always disconnect the battery before working on any electrical components.
- Avoid working on electrical systems in wet or damp conditions to prevent electric shock.
- Use insulated tools and wear protective gear, such as gloves and safety goggles, when handling electrical components.
Chevy 350 Starter Wiring Diagram
How To Wire Starter On Chevy 350

Starter Wiring For Chevy 350

Simple Chevy 350 Starter Wiring Diagram

Chevy 350 Starter Wiring Diagram
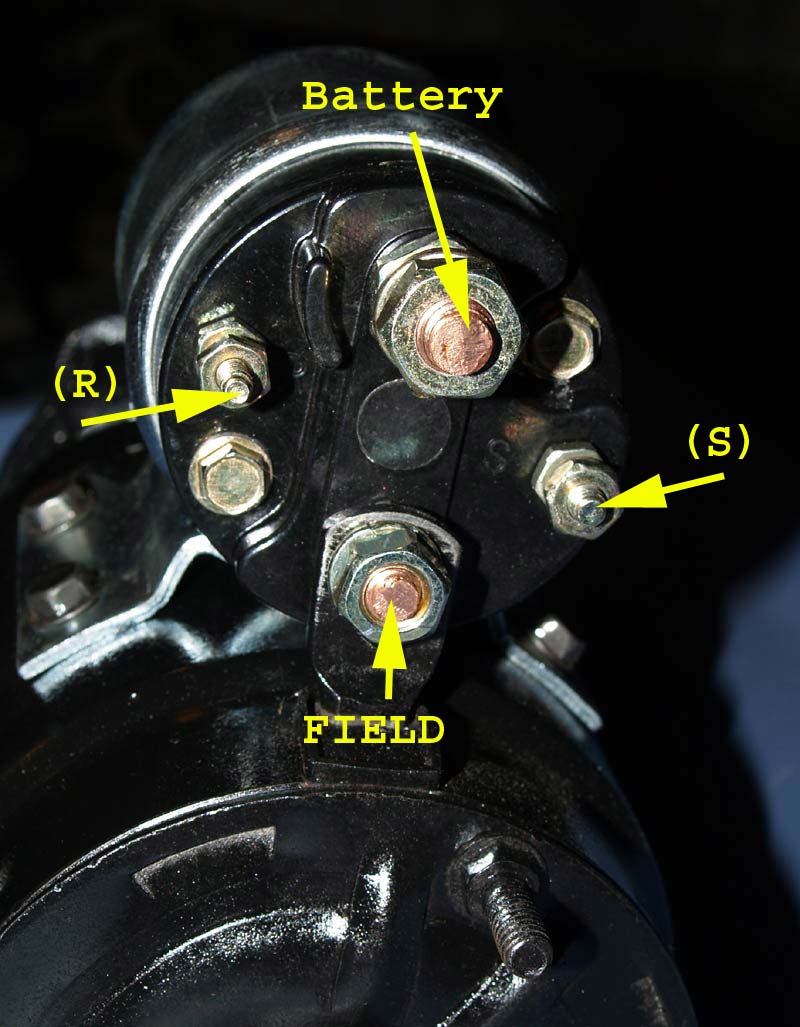
350 Chevy Starter Wiring Diagram

Starter Wiring Diagram Chevy 350

Simple Chevy 350 Starter Wiring Diagram

Wiring Diagram Chevy 350 Starter
