Introduction
Basic Race Car Wiring Diagram is a crucial component in the construction and maintenance of race cars. It serves as a roadmap for the electrical system of the vehicle, helping to ensure that all the components work together seamlessly. Understanding how to read and interpret these diagrams is essential for any mechanic or enthusiast looking to work on a race car.
Importance of Basic Race Car Wiring Diagram
Basic Race Car Wiring Diagram are essential for several reasons:
- They provide a visual representation of the electrical system, making it easier to understand how everything is connected.
- They help in locating specific components and understanding their function within the system.
- They serve as a reference guide during installation, repair, or modification of the electrical system.
Reading and Interpreting Basic Race Car Wiring Diagram
Reading and interpreting Basic Race Car Wiring Diagram effectively requires the following steps:
- Start by identifying the key components in the diagram, such as the battery, alternator, ignition switch, and various sensors.
- Follow the lines connecting the components to understand the flow of electricity through the system.
- Pay attention to symbols and color codes used in the diagram to differentiate between different types of wires and components.
Using Basic Race Car Wiring Diagram for Troubleshooting
Basic Race Car Wiring Diagram are invaluable tools for troubleshooting electrical problems in race cars. Here’s how they can help:
- By following the diagram, you can identify the root cause of an electrical issue and pinpoint the faulty component.
- You can test the continuity of wires and check for any shorts or open circuits using the information provided in the diagram.
Importance of Safety
When working with electrical systems and using wiring diagrams, safety should always be the top priority. Here are some safety tips and best practices to keep in mind:
- Always disconnect the battery before working on any electrical components to prevent the risk of electric shock.
- Use insulated tools and wear protective gear, such as gloves and goggles, to protect yourself from potential hazards.
- Double-check your work and ensure all connections are secure before reassembling the components and turning on the power.
Basic Race Car Wiring Diagram
Understanding Basic Race Car Wiring Diagrams – Moo Wiring

Basic Wiring 4 Cylinder Race Car

Proper Racecar Wiring Principles – Davis Technologies

Basic Race Car Wiring Diagram For Your Needs
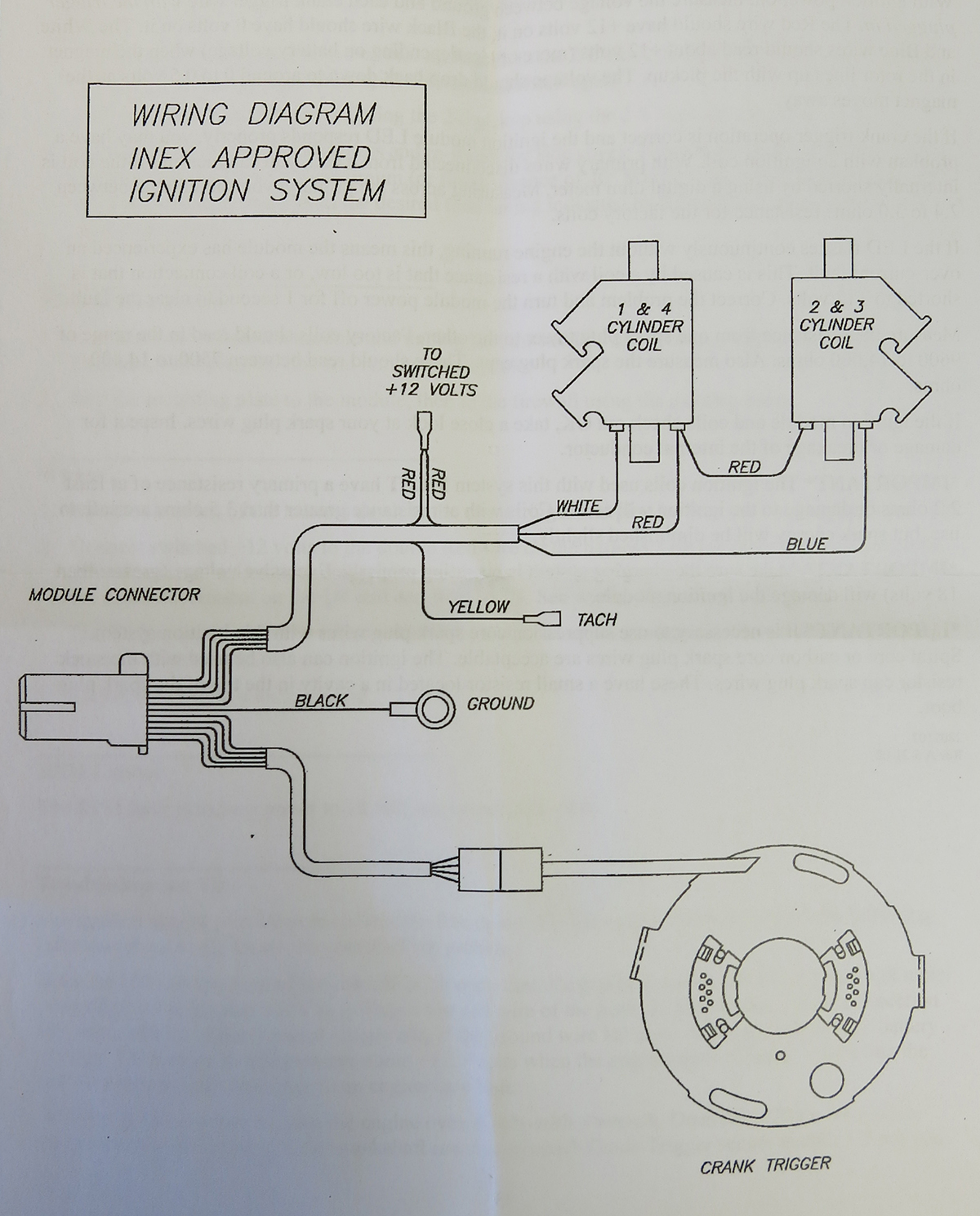
basic race car wiring diagram – Wiring Diagram and Schematics

[36+] Bugatti Wiring Diagram One Switch, 31 Race Car Push Button Start
![Basic Race Car Wiring Diagram [36+] Bugatti Wiring Diagram One Switch, 31 Race Car Push Button Start](http://ls1tech.com/forums/attachments/conversions-hybrids/107840d1192753875-ls1-race-car-wiring-batt-alt-disconnect-battery_disconnect.gif)
Race Car Wiring Setup – Wiring Diagram Detailed – Basic Race Car Wiring

Basic Wiring Diagram For Race Car – Wiring Digital and Schematic
