Are you looking to understand the intricacies of a 4 Pin Alternator Wiring Diagram? These diagrams are crucial for anyone working with electrical systems in vehicles, providing a roadmap for connecting the alternator to the battery and other components. Let’s delve into the importance of these diagrams and how to effectively interpret them.
Why are 4 Pin Alternator Wiring Diagrams Essential?
4 Pin Alternator Wiring Diagrams are essential for several reasons:
- They provide a visual representation of how the alternator is connected to the battery and other electrical components.
- They help ensure that the wiring is done correctly, preventing electrical issues and potential damage to the vehicle.
- They serve as a guide for troubleshooting electrical problems and making repairs.
How to Read and Interpret 4 Pin Alternator Wiring Diagrams
Reading and interpreting 4 Pin Alternator Wiring Diagrams may seem daunting at first, but with some guidance, it can become second nature:
- Start by identifying the different components in the diagram, such as the alternator, battery, and various connectors.
- Follow the lines to understand how the components are connected and the flow of electricity.
- Pay attention to color coding and symbols used in the diagram to decipher the information more easily.
Using 4 Pin Alternator Wiring Diagrams for Troubleshooting
4 Pin Alternator Wiring Diagrams are invaluable when it comes to troubleshooting electrical problems in vehicles:
- By comparing the actual wiring to the diagram, you can pinpoint any discrepancies or faulty connections.
- You can use the diagram to test the continuity of wires and ensure that electricity is flowing correctly.
- Identifying the root cause of electrical issues becomes much easier with a clear understanding of the wiring diagram.
Importance of Safety
When working with electrical systems and wiring diagrams, safety should always be a top priority:
- Ensure that the vehicle’s battery is disconnected before working on any electrical components.
- Avoid working on the electrical system in wet or damp conditions to prevent the risk of electrocution.
- Use insulated tools and wear protective gear, such as gloves and safety goggles, when handling electrical components.
4 Pin Alternator Wiring Diagram
4 Pin Gm Alternator Wiring Diagram | Wiring Library – Chevy Alternator

4 Pin Alternator Wiring Diagram

4 Wire Alternator Wiring Diagram – Wiring Digital and Schematic

Alternator Wiring Diagram External Regulator

Toyota Alternator Wiring Diagram – Yarnish
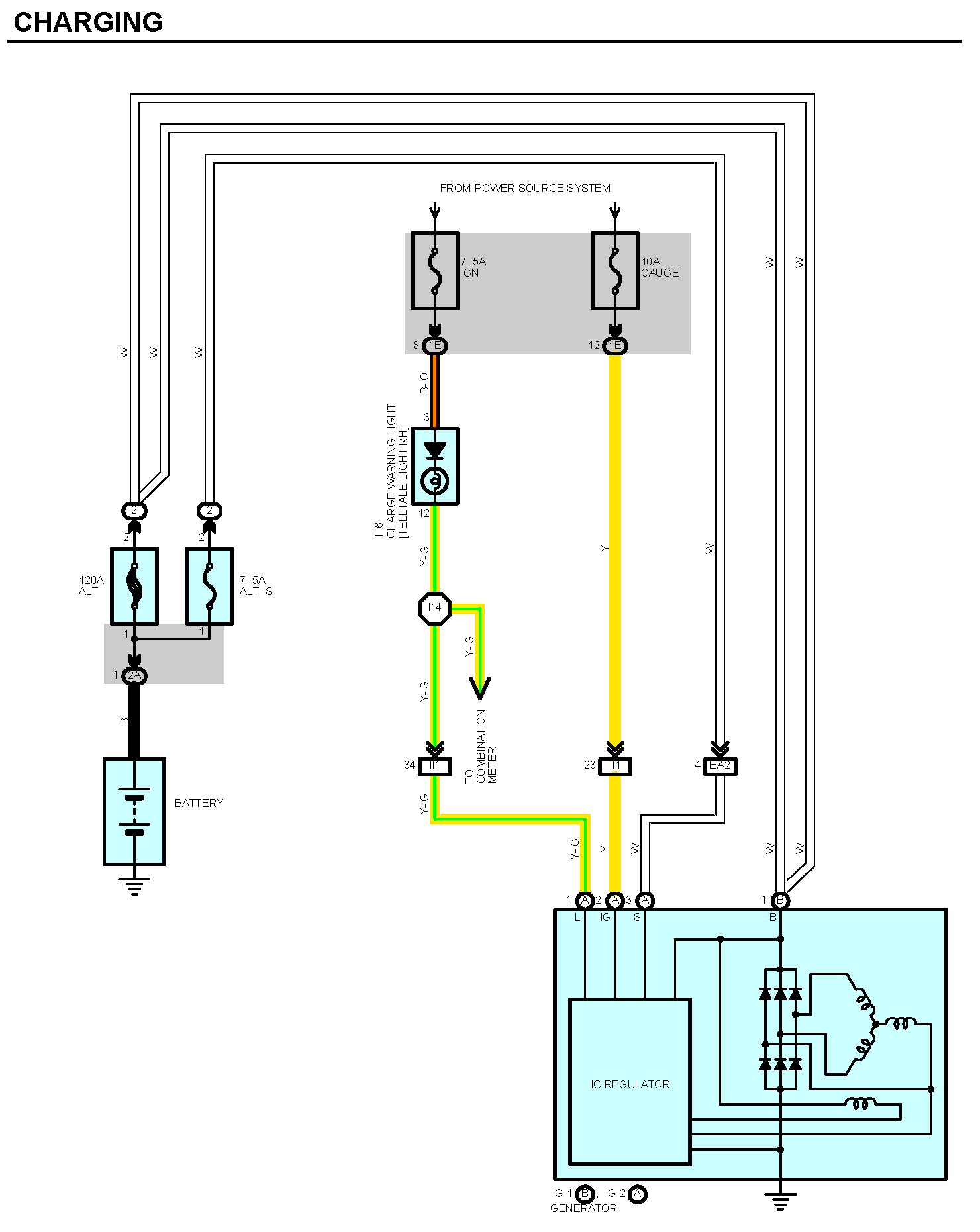
4 Pin Alternator Wiring Diagram – Knittystash.com

Gm Alternator Wiring Diagram Pcm

Honda 4 Pin Alternator Wiring Diagram
